mmWave

mmWave communication refers to 5G communication in the mmWave frequency band, which has a frequency range of 24.25-52.6 GHz and is also known as the FR2 band defined by 3GPP. By leveraging the advantages of large bandwidth and low latency in the mmWave frequency band, countries such as the United States have already deployed 5G mmWave commercial networks and provided contiguous coverage in hotspot areas. Tests have shown that the peak cell rate of mmWave networks far exceeds that of the mid-band frequencies in 5G.
In terms of high-speed and high-efficiency transmission, mmWave communication can be used in large venues, shopping malls, transportation hubs, office buildings, AR remote guidance, 8K ultra-high-definition video transmission, and other scenarios. In terms of low-latency communication, mmWave communication can be used in remote device control, AR/VR real-time interactive games, and other scenarios.
Flexible networking options such as NR-DC (dual connectivity), FR2-Only, and CA (carrier aggregation) can be selected based on application requirements. For the FR1+FR2 NR-DC networking mode, the mid-band and mmWave frequency band resources are efficiently utilized, with the FR1 frequency band providing network coverage continuity and the mmWave frequency band providing ultra-high-speed data transmission, improving user service experience. For the millimeter wave+CA networking mode, the transmission bandwidth of the mmWave frequency band is further improved, achieving a system capacity that is five times or higher than Sub6G.
The mmWave frequency bands defined by 3GPP:
|
Band No. |
Frequency |
Duplex |
|
n257 |
26500 MHz – 29500 MHz |
TDD |
|
n258 |
24250 MHz – 27500 MHz |
TDD |
|
n259 |
39500 MHz – 43500 MHz |
TDD |
|
n260 |
37000 MHz – 40000 MHz |
TDD |
|
n261 |
27500 MHz – 28350 MHz |
TDD |
|
n262 |
47200 MHz – 48200 MHz |
TDD |
|
n263 |
57000 MHz – 71000 MHz |
TDD |
Key technologies enabled by 5G mmWave communication include Beamforming, Beam Management, Flexible Frame Structure, and NR-DC.
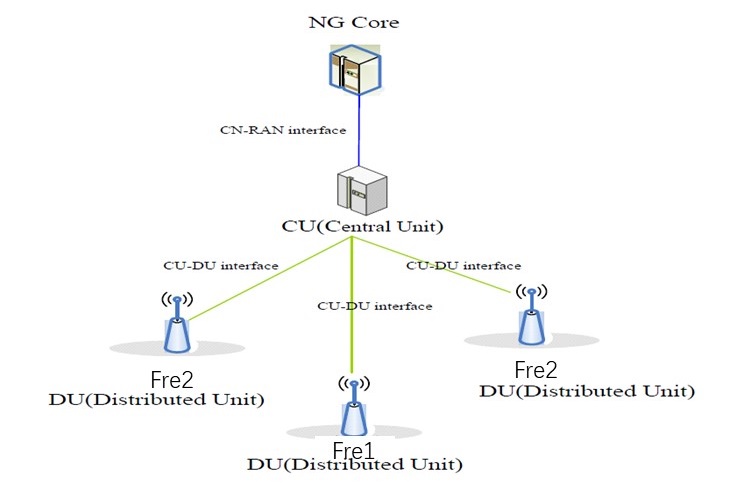
Figure 2 NR-DC Network Topology (FR1+FR2)
mmWave network capabilities:
Subcarrier spacing of 120 kHz
Time slot length of 0.125 ms, with data transmission and scheduling time 25% of that of Sub6G communication, significantly reducing latency
Frequency bands: support for N257 and N258 bands
Flexible frame structure: support for DDDSU, DSUUU, and DDSUU
Support for beamforming and beam management, enhancing network coverage
Compact Massive MIMO antenna arrays
Support for NR-DC dual connectivity (FR1+FR2)
Support for carrier aggregation (CA)
Advantages of mmWave solutions: large bandwidth, end-to-end latency <5ms, high capacity and high data rates, improved communication services in hotspots, support for multiple networking modes, support for higher-precision positioning.
Application scenarios: large venues, shopping malls, airports, train stations, office buildings, hotels
Related products: mmWave base stations, URLLC technology, NR-DC technology.
Key technologies enabled by 5G mmWave communication include Beamforming, Beam Management, Flexible Frame Structure, and NR-DC.
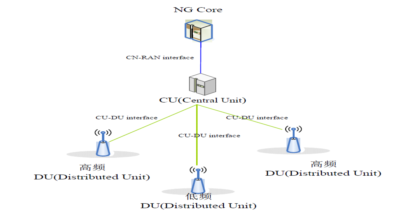
mmWave network capabilities:
- Subcarrier spacing of 120 kHz
- Time slot length of 0.125 ms, with data transmission and scheduling time 25% of that of Sub6G communication, significantly reducing latency
- Frequency bands: support for N257 and N258 bands
- Flexible frame structure: support for DDDSU, DSUUU, and DDSUU
- Support for beamforming and beam management, enhancing network coverage
- Compact Massive MIMO antenna arrays
- Support for NR-DC dual connectivity (FR1+FR2)
- Support for carrier aggregation (CA)
Advantages of mmWave solutions:
large bandwidth, end-to-end latency <5ms, high capacity and high data rates, improved communication services in hotspots, support for multiple networking modes, support for higher-precision positioning.